Augmented Reality (AR) Technologies: From Gaming to Medicine
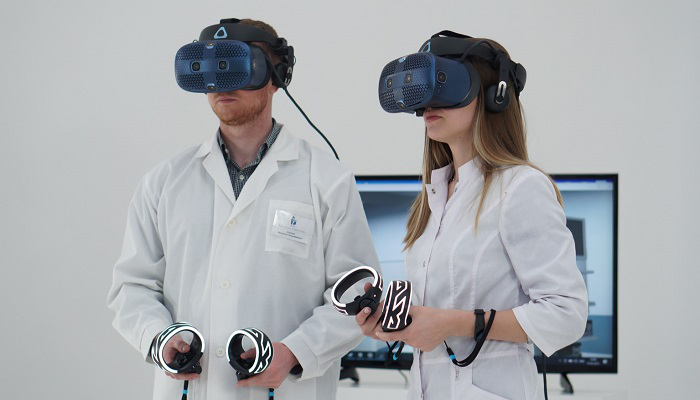

Augmented Reality (AR) is a technology that overlays virtual objects and information onto an image of the real world. In recent years, AR has expanded beyond the entertainment industry and has found its application in important areas such as medicine, education, and cultural projects.
Using AR in Games
Augmented reality initially gained widespread adoption thanks to the gaming industry. One of the most striking examples is the game Pokémon GO, where players can use their smartphones to interact with virtual creatures in the real world. AR allows players to feel like active participants in events, creating immersive experiences.
Today, AR technologies are used in a wide range of gaming projects – from quests with virtual clues in real locations to multiplayer games where virtual objects are integrated into physical space. The main advantage of AR in games is that it breaks down the boundaries between the virtual and real worlds, giving players a unique experience of interacting with the environment.
AR in training and education
Augmented reality technologies have become an important tool in education, making the learning process more interactive and visual. For example, with the help of AR, students can visualize complex concepts such as the structure of molecules, human anatomy, or historical events.
Educational applications using AR allow you to create virtual models that can be viewed and interacted with in real time. For example, students can explore the structure of cells using AR applications that project 3D models onto work surfaces. This approach contributes to a deeper assimilation of the material, since learning becomes not only theoretical but also practical.
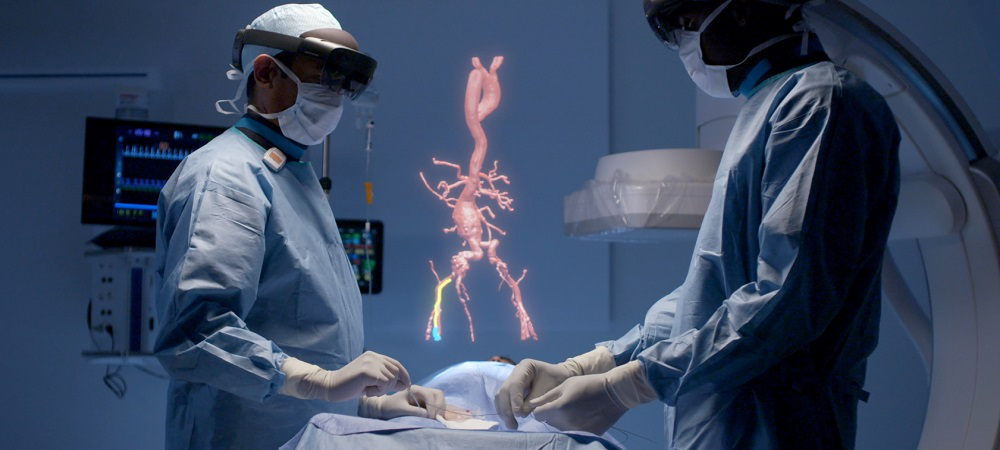
Medical simulations using AR
In the medical field, AR is actively used for simulations and training of future doctors. The technology allows projecting virtual organs or surgical instruments onto patients’ bodies, which helps students study anatomy and practice surgical skills without risk to real patients.
In addition, AR is used in real surgeries to improve the accuracy of interventions. Surgeons can use special AR glasses that overlay information about the patient directly on their body, showing important data such as the location of organs or vessels. This improves visualization and helps surgeons make more accurate decisions during operations.
Virtual exhibitions and cultural projects with AR
Augmented reality also finds its application in the cultural sphere. Museums and exhibition halls use AR to create interactive exhibits. For example, visitors can use smartphones or tablets to get additional information about the exhibited objects, see them in 3D or recreated in their original form.
AR exhibitions allow visitors not only to enjoy works of art, but also to interact with them, gaining new experiences that cannot be achieved using traditional methods. Virtual tours, animations, and interactive objects make visiting cultural events more memorable and educational.
Augmented reality (AR) technologies play an important role in a variety of fields, from gaming and education to medicine and cultural projects. AR helps create new forms of interaction with virtual objects, improves educational processes and medical procedures, and opens up new horizons for art and entertainment. In the future, we can expect even greater implementation of AR in our daily lives, where the virtual and real worlds will increasingly intersect.


